Read time 3 minutes
If you are an Exchange Administrator, you might have come across several orphaned or disconnected mailboxes. A disconnected mailbox is a mailbox object residing in an Exchange mailbox database that isn’t linked to an Active Directory user account. The disconnected mailbox has a retention period of 30 days. After that, the mailbox will be permanently deleted. Therefore, to safeguard the data, many organizations export it.
Exporting a normal mailbox is a simple process. You can do it with Exchange Admin Center (EAC) or using the Exchange Management Shell (EMS). However, the steps to export disconnected Exchange mailboxes to PST are not the same as for a connected mailbox. You need to have the mailbox connected to an Active Directory account to export it.
Prerequisites to Export Disconnected Exchange mailboxes to PST
To avoid any interruption during mailbox export, you must take care of the following points.
- Permissions: To export a mailbox, you need to have the Mailbox Import Export Role assigned. Ask your administrator to do it for you or use the following EMS command to do it.
- New-ManagementRoleAssignment –Role “Mailbox Import Export” –User
Note:You might have to wait for a while after assigning the role. Sometimes, the role assignment takes time and is not instant. - UNC Path: Exporting the mailboxes directly to a local drive on the Exchange Server is not possible. When you export disconnected Exchange mailboxes to PST, you must save it to a Universal Naming Convention (UNC) path like:
(\ < Server >\ < Share >\ or \ < LocalServerName >\c$)
- Find the Mailbox to Recover: The orphaned mailboxes only stay in the database till their retention period. Therefore, you must check and verify if the required mailbox is still present in the database. If it is permanently purged, then you have to recover deleted mailbox from Exchange.
- Temp Active Directory User Account: To Export Disconnected Exchange mailbox, you must first connect it to an Active Directory Account. Use an old account or create a temporary AD account. Then, connect the mailbox with the user account and restore it.
How to Export Disconnected Exchange Mailboxes to PST?
If the mailbox is still in the retention period and you have connected it to a temporary Active Directory account, you can begin exporting it. To export mailboxes, we have two native solutions.
Method 1: Export Using Exchange Admin Center (EAC)
Exchange Admin Center allows users to manage complete Exchange Server functions without working with complex commands. With EAC you can easily create a new export request with the following steps:
Step 1: Go to EAC and click on the recipients option in the left pane.
Step 2: Click on the mailboxes tab and select the mailbox you want to export.
Step 3: After selecting the mailbox, click on the More options icon and click Export to a PST file.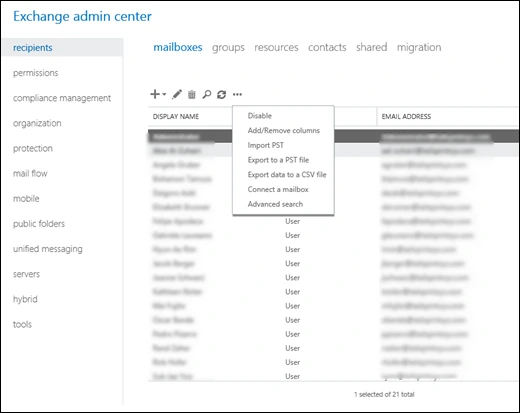
Step 4: In the Export to a .pst file wizard, click Browse and select the source mailbox. Choose one of the following export options and click Next
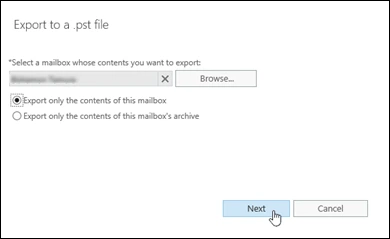
Step 5: Provide the UNC path and the filename of the PST file that will be saved on the specified path.
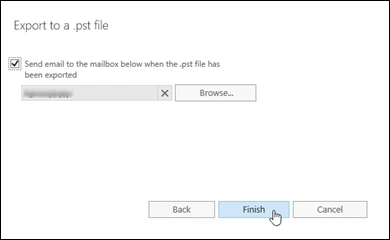
Step 6: You can choose to leave or send an email to the mailbox after export. If you want an email, then click Browse and specify the recipients of the email. Finally, click Finish to start the export process.
Method 2: Export Using Exchange Management Shell (EMS)
Users who have technical knowledge of Exchange Management Shell can export the mailboxes using EMS commands. Using the EMS commands to export disconnected Exchange mailboxes to PST is quicker in comparison to the above method. This command line-based method is only for people who understand the command line interface of Exchange. Execute the command given below:
New-MailboxExportRequest -Mailbox “mailbox-name” -FilePath“UNC-file-path”
In the above command, replace the “mailbox-name” with the mailbox you want to export. Similarly, replace the “UNC-file-path” with the path where you want to save the .pst file after export.
To export only the content of an individual folder you can use the following command:
New-MailboxExportRequest -Mailbox “mailbox-name” -FilePath “UNC-file-path” -IsArchive -IncludeFolders “#Inbox#”
Note: After successfully exporting the mailboxes, delete the temp Active Directory Account.
Quickly Export Disconnected Exchange Mailboxes to PST From Corrupt EDB File
Manual methods require healthy Exchange database files to save emails to PST. But what will you do if your EDB file is damaged or not mounted? In such a case, you must use a third-party EDB to PST tool. Kernel for Exchange Server is an advanced tool that allows users to export mailboxes from offline EDB files, Exchange On-Premises and Office 365 accounts.
The Exchange recovery tool is embedded with robust algorithms that deeply scan the EDB file and can even recover lost/deleted emails. Users can view complete mailbox data in the tool and can apply various filters for selective data conversion. Export mailboxes from unlimited EDB files with complete data integrity and original items & folder structure.
Conclusion
In this blog, we discussed how you can export disconnected Exchange mailboxes to PST. Use the EAC or EMS to safely export mailboxes. However, before you begin the export, connect the mailbox to a temp AD account. To export mailboxes from corrupt or dismounted Exchange databases, use Kernel for Exchange Server. The tool is powered with dual scanning modes – Standard Scan & Deep Scan. Use the Exchange database recovery tool to easily restore data from severely corrupted EDB files







