Read time 7 minutes
Encountering scenarios where two similar mailboxes coexist within the same Exchange Database is quite common in an Exchange server environment. Typically, one mailbox is actively used while the other lies dormant. Exchange Server allows the option to eliminate redundant mailbox using the “remove-mailbox” cmdlet. It’s vital to note that when you delete a mailbox from the Exchange database, the associated user information is also removed from the Active Directory. Therefore, if your intention is solely to deactivate the user’s mailbox, you should opt to disable it instead.
Process to disable the user mailbox in Exchange database
Here is the brief procedure to disable user mailbox from the Exchange database:
- Log in to the Exchange Admin Center with the Administrator credentials.
- Under recipients, go to mailboxes, select the user mailbox to be disabled, click more (•••) and click Disable.
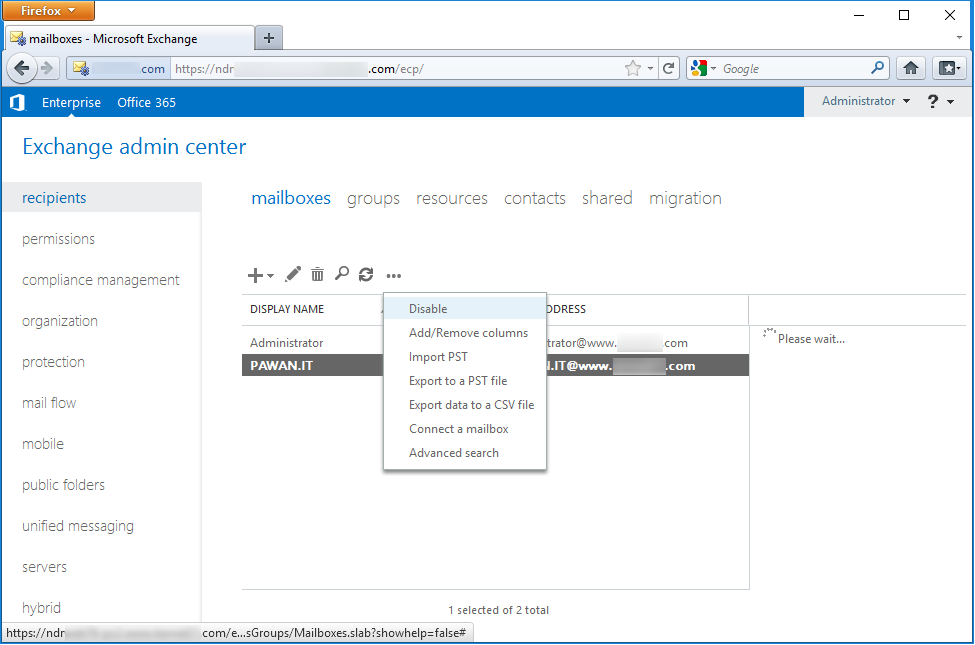
- A warning message will appear. Click Yes.
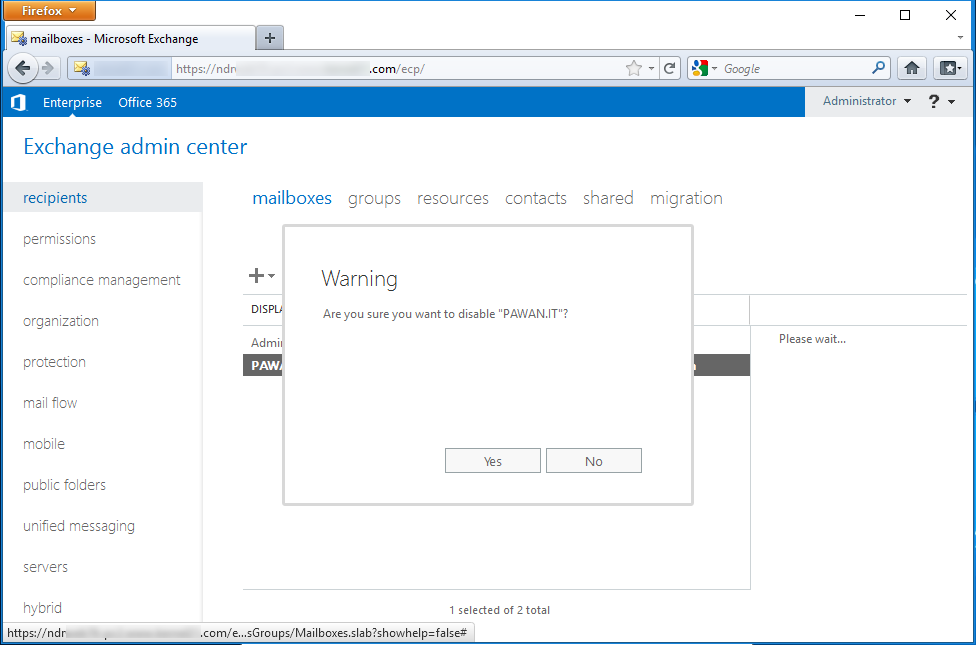
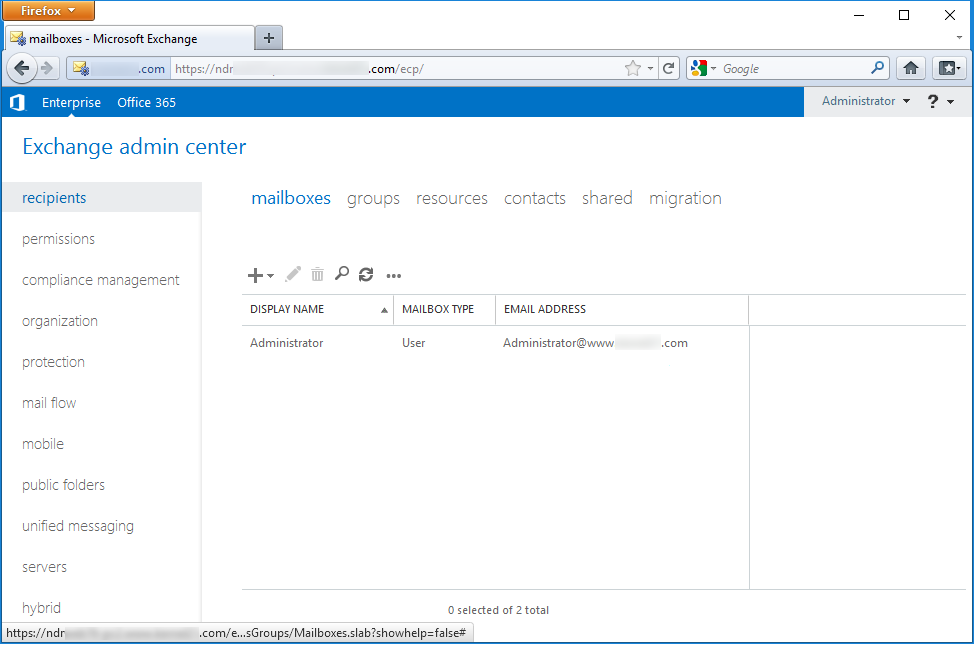
- The user mailbox will disappear from the list; and after the expiry of the retention period, the mailbox will be deleted permanently.
Use Exchange Management Shell to disable a mailbox
You can disable a mailbox using Exchange PowerShell command:
Disable-Mailbox <MailboxName>
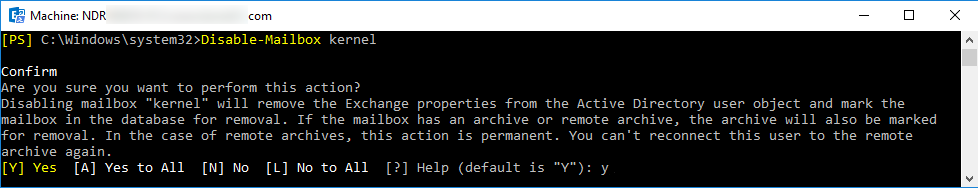
When you run the command, it will ask you to confirm your action. After confirmation, it will delete the mailbox.
Delete a mailbox with Exchange admin center
Here is a step-by-step process for deleting an Exchange Server mailbox:
- Login to EAC using the administrator credentials and then go to Recipients.
- Select the type of mailboxes from the list:
- Mailboxes: user and linked mailboxes
- Resources: equipment mailboxes
- Shared: shared mailboxes
- Public folder: public folder mailboxes
- Find and select the mailbox(es) you want to delete from the list of mailboxes.
- After choosing the mailboxes, click Delete and Yes in the warning message dialog box.
Delete mailbox using Exchange Management Shell
When deleting Exchange mailboxes, you might sometimes need to remove a single mailbox or multiple mailboxes from the database. It is important to ensure that you have the required permissions to remove the mailbox(es) and be aware that you are deleting the right mailboxes from the EDB.
How to delete a single mailbox in Exchange Server?
Use the following cmdlet to delete a single mailbox from Exchange Server:
Remove-Mailbox
This cmdlet performs soft deletion of a single mailbox from Exchange database. This means that a mailbox is removed and will be deleted permanently once the retention period (default is 30 days) of the deleted mailbox expires. You can check the retention period using the following command:
Get-MailboxDatabase | FL -Property PSComputerName,MailboxRetention
How to delete multiple mailboxes from Exchange Server?
Use the following cmdlet in a pipeline to remove multiple mailboxes from Exchange Server.
Get-DistributionGroupMember
Use the given command to delete inactive mailboxes from the database:
Get-Mailbox -ResultSize Unlimited –RecipientTypeDetails UserMailbox,SharedMailbox | Where {(Get-MailboxStatistics $_.Identity).LastLogonTime -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(-90)} | Remove-Mailbox -whatif
This script removes all the inactive mailboxes that have been inactive for more than 90 days duration. It’s crucial to remove all of them from the server.
How to delete a disconnected mailbox permanently?
All the disabled and soft-deleted mailbox are known as disconnected mailboxes. You can either reconnect or permanently delete the disconnected mailboxes. Below mentioned Exchange Management Shell script will help to identify if the disconnected mailbox belongs to soft-deleted or disabled category.
$dbs = Get-MailboxDatabase $dbs | foreach {Get-MailboxStatistics -Database $_.DistinguishedName} | where {$_.DisplayName -eq “”} | Format-List DisplayName,MailboxGuid,Database,DisconnectReason
Use the following cmdlet to delete disabled mailbox(es) permanently:
Remove-StoreMailbox -Database MBD55 -Identity “2ab56ce7-afc8-3343-8996-d87e3fe189c3” -MailboxState Disabled
Use the following cmdlet to delete soft-deleted mailbox(es) permanently:
Remove-StoreMailbox -Database MBD55 -Identity “Alex Johnson” -MailboxState SoftDeleted
How to recover a deleted mailbox?
Within the Exchange environment, the accidental deletion of valuable mailboxes is a potential concern. Fortunately, Exchange Server offers built-in methods for recovering deleted data. Alternatively, you can use a specialized professional tool capable of managing both healthy and corrupted Exchange data, securely storing it in an alternate location or another platform. This tool also proves invaluable for safeguarding mailboxes by creating backups before their removal from the Exchange database.
Kernel for Exchange Server is a powerful utility designed to eliminate corruption within the Exchange database, seamlessly restoring every mailbox and its contents. You can use the edb recovery software to take backups, extract/export mailbox data, and migrate to an upgraded version of Exchange Server.
Conclusion
Managing unwanted mailboxes in the database can enforce a significant challenge for an Exchange Administrator. Fortunately, these mailboxes can be removed without affecting the associated user accounts. Prior to deletion, you have the option to safeguard their data by effortlessly creating a PST file using Kernel for Exchange Server mailbox recovery tool. You can also use this tool to Export EDB to PST file within a matter of minutes, streamlining the entire procedure.







