Read time 6 minutes
Exchange Server follows the Transport Layer Security to communicate with internal servers and various Exchange services. But it also requires communicating with external clients regularly, and therefore different kinds of digital certificates are used. A digital certificate verifies the identity of the Exchange Server or user account. In an on-premises Exchange Server, there are three self-signed digital certificates used to validate the connections with various services and external clients. One such certificate is the ‘Microsoft Exchange Server Auth Certificate.’
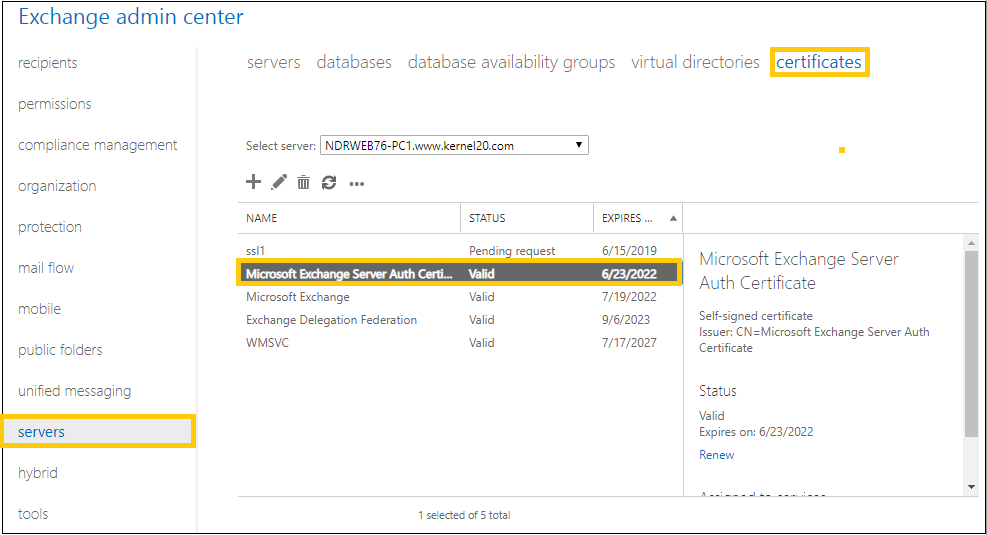
The Auth Certificate is helpful in server-to-server authentication and integration with SharePoint Server and Skype for Business. You can check all certificates in the Certificates category under servers in Exchange Admin Center.
What is an Auth Certificate in Exchange Server?
The Auth Certificate is an Exchange Server’s utilized certificate helpful in server-to-server authentication and integration with SharePoint Server and Skype for Business. You can check all certificates in the Certificates category under servers in the Exchange admin center.
You can run the following command in Exchange Management Shell to check the status of your certificate:
(Get-AuthConfig).CurrentCertificateThumbprint | Get-ExchangeCertificate | Format-List Subject, Thumbprint, NotAfter, NotBefore
When you first install Exchange Server on your system, the setup automatically generates a certificate with the name “Microsoft Exchange Server Auth Certificate.”
What are the practical benefits of an Auth Certificate?
Here are some advantages of Exchange Auth Certificate that make it substantial to resolve the error “auth certificate missing.”
- It is a standard authentication protocol essential for all Exchange environments.
- Requires nominal efforts to manage once they are set up and renewed periodically.
- Helps in encrypting sensitive information.
- Provides a secure environment for communication.
In addition to the above points, these certificates prevent unauthorized account access, a dangerous but not so uncommon occurrence in large enterprises. Such a situation can lead to data loss and require immediate solutions like the use of an Exchange data recovery tool.
‘Auth Certificate Missing’ issue
Many user queries say that they have a successful deployment of their Exchange Server version, but when they try to access OWA, an error pops up like this.
‘Federation or Auth certificate not found: “Certificates-thumbprint.” Unable to find the certificate in the local or neighboring sites. Confirm that the certificate is available in your topology and if necessary, reset the certificate on the Federation Trust to a valid certificate using Set-FederationTrust or Set-AuthConfig. The certificate may take time to propagate to the local or neighboring sites.’
The error itself describes that the certificate is missing or cannot be configured. This disturbs the server to server authentication and communication and even blocks accessing those servers.
The situation becomes worse when you need some crucial information, but the server won’t allow you to access it. To prevent the delay, Exchange admins create a backup of the server data either with passive database copies or with an EDB to PST converter tool.
Fix Microsoft Exchange Server Auth certificate missing error
This issue of missing Exchange Server Auth Certificate can be resolved by creating a new certificate by running cmdlets in the Exchange Management Shell. The process of running cmdlets requires technical knowledge as well as great care to avoid any further errors. Also, the user must have Exchange administrator rights to perform this procedure. If you have all these pre-requisites completed, start the process as instructed below:
Step 1. Open the Exchange Management Shell on your Exchange 2016/2013 server.
Step 2. Run this command to create a new Exchange Auth certificate.
New-ExchangeCertificate -KeySize 2048 -PrivateKeyExportable $true -SubjectName “CN= Microsoft Exchange Server Auth Certificate” -DomainName “*.enterdomainname.com” -FriendlyName “Microsoft Exchange Server Auth Certificate” -Services SMTP
For example:
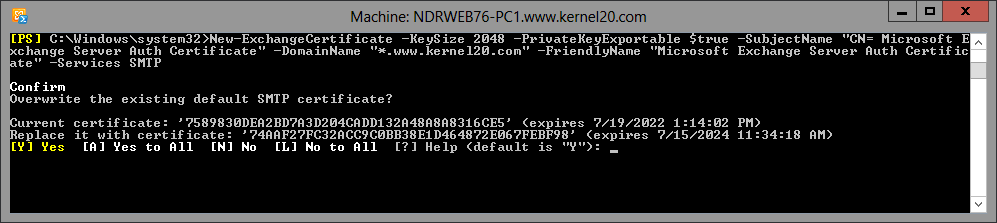
Step 3. Once the above command is run, it will ask you if you want to overwrite the existing default SMTP certificate. Type N and press Enter.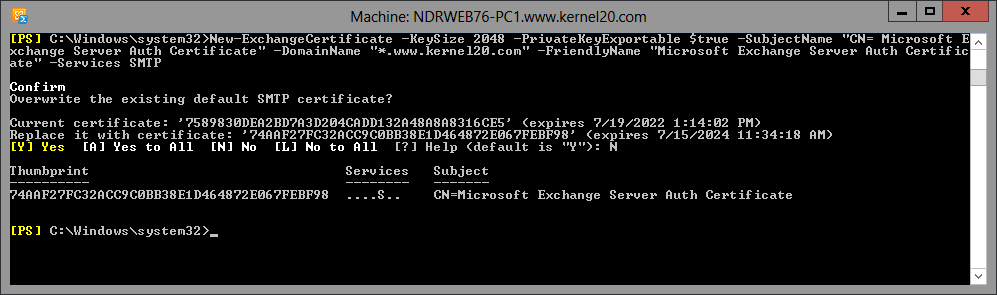
A certificate thumbprint will get created here as output of the command. You need to note down this alpha-numeric certificate thumbprint somewhere, as you would require it in the next cmdlet.
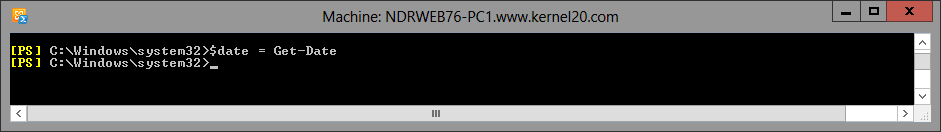
Step 4. Run this next command to save the present date to the object.
$date = Get-Date
Step 5. Now, to set the authentication configuration for Exchange, execute the following cmdlet.
Set-AuthConfig -NewCertificateThumbprint <certificate_thumbprint> –NewCertificateEffectiveDate $date
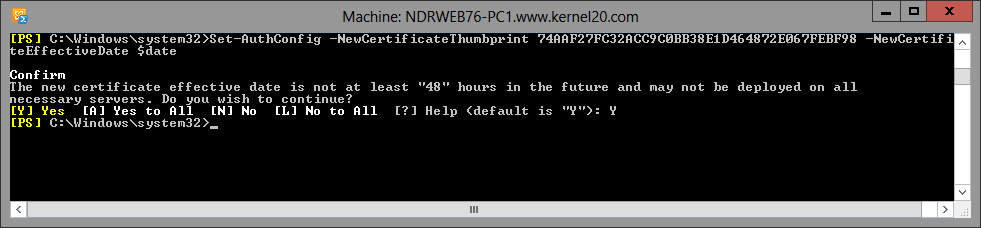
When you execute the above command, it asks to confirm regarding the effective date of the certificate. Confirm it by typing Y and pressing Enter.
Step 6. Next command should be run to publish the newly created Exchange Auth certificate.
Set-AuthConfig –PublishCertificate
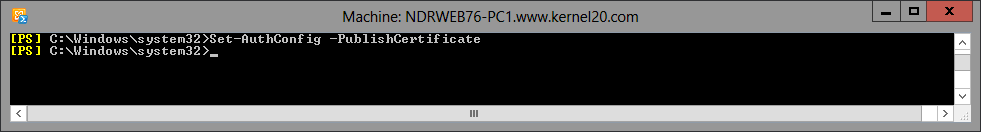
Note: If you have any previously installed Exchange certificate, you need to clear it with the following command.
Set-AuthConfig -ClearPreviousCertificate
Step 7. Finally, run this cmdlet to reset the ISS service for all CAS and mailbox servers.
IISRESET
Thus, you can fix the error ‘the Exchange Auth Certificate is missing.’ To save yourself from receiving this error, you can regularly check the expiration period of the certificate.
What happens when you implement manual approaches?
As the error was technical, the method explained above requires technical skills and expert guidance to perform it successfully. One should be familiar with running the cmdlets in the Exchange Management Shell to accomplish the desired result from the above process.
Apart from this error, there are many other Exchange errors and issues administrators face in the Exchange environment. We recommend the Exchange users stuck in these situations to go for the best Exchange data repair solution.
Kernel for Exchange Server is the best Exchange EDB recovery tool which deals with all problems or errors related to the Exchange database and recovers inaccessible Exchange mailboxes to various destinations like PST, Live Exchange, Microsoft 365, etc. The tool maintains the integrity of the Exchange data after the recovery and allows users to make a selection of data using the filter options before saving it to the desired location.
Summing up
With the procedure explaining how to resolve the Exchange Server Auth Certificate missing problem, you will be able to access the mailbox without facing an issue. You can also apply for a new certificate from Microsoft and if the error still persists and affects the Exchange Kernel for Exchange Server software is the best go-to solution to recover the mailbox and save it in a new Exchange account.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ans. It depends on the number of services that rely on that certificate. Usually, it takes at most 24 hours. After that, you will not have any issue accessing the servers that use these certificates for authorization.
Ans. To prevent such errors from disturbing your work, you need to monitor and check certificates for expiry or misconfiguration periodically. Alternatively, you can set up a mechanism that helps to identify certificates whose expiration dates are near.
No, the Auth Certificates are stored in Active Directory, and a corrupt EDB will not give Auth Certificate-related errors. However, corrupt EDB files can prevent you from accessing OWA. If you think corruption is the culprit, use a professional tool to repair EDB files.








