Read time: 8 minutes
Data is the most essential part of every organization, so the tools we use in the workplace must ensure data security and protect data integrity, mainly collaboration and communication tools like Microsoft Teams.
Teams is a collaboration platform facilitating several team management tasks such as video conferencing, audio & video calls, monitoring, task assignment, messaging, channels, posts, notes, and more. Users can also share important files or documents over Teams.
Because of all these advanced features, Teams is currently the most popular collaboration and video conferencing tool among organizations. But cases like BlueBleed data leak (October 2022) and accidental data exposure by AI researchers (September 2023) have compromised multiple TBs of data. Such incidents raise the question– how secure is Microsoft Teams?
This post will discuss different aspects of Microsoft Teams security and what we can do to keep it secure while still maximizing end-user collaboration service.
Reasons behind Microsoft Teams security being a top priority
Before moving further in the blog, it’s important to know why Microsoft Teams Security is among hot topics. So, below are a few reasons behind it:
- Teams act as an entry point into your business.
- Teams increasing popularity and the growing user base are attractive targets for bad actors.
- Business continuity and growth now depend on Teams as it provides seamless communication, collaboration, and meeting services.
- Teams’ variety of features makes life easier for your employees, but it also gives rise to more reasons for potential attacks.
How was security managed before cloud?
Before cloud computing, the firewall configuration was the key pillar for security, and you used to rely on an organization’s firewall as a secure perimeter. All the servers, such as the application server, Exchange Server, SharePoint Server, file server, and Skype for Business Server, run behind a firewall in your data center.
But the advent of cloud services like Office 365 made everything easy and started allowing users to work and communicate over files outside the data center. Now companies aren’t required to depend on their servers and firewalls as they can subscribe to Cloud services for applications like Exchange, SharePoint, OneDrive, Office 365, etc. Cloud security services are much better than a firewall. And the security of Microsoft Teams goes beyond that.
Is Microsoft Teams secure?
The answer to this question is – Yes. Undoubtedly, Microsoft Team is designed to be highly secure. It ensures that file sharing and communication occur among known and authorized users who have data access.
But just as we have to lock the doors of our house, we need to employ the lock in Office 365 so that it strikes the perfect balance between ease of use and security.
Before moving to it, firstly, let’s discuss what can be a security threat to Microsoft Teams. Below are some significant threats:
- External Access or Guest Access.
- Access from untrusted locations or unmanaged devices.
- Malware uploaded through Microsoft Teams.
- Sharing and displaying confidential data.
- Data loss through Microsoft Teams chat, file shares, and other applications.
- Data residency
Best practices to secure Microsoft Teams
There are several ways to enhance Teams’ security and minimize the security risks. Some of Microsoft Teams’ best security practices are listed below:
Define Microsoft Teams Governance
Teams’ governance policies are one of the best ways to enforce security. These policies determine how the organization will perform internally, how the end-users will use the app, who can create Teams accounts, and what information or data users can share. It’s essential to appoint a Teams administrator to implement governance policies across the organization.
When it comes to security, you can also consider these points:
- Who can Create Teams?
The first and the most important thing is to decide who can create a Team in Microsoft Teams because it will allow you to reduce teams sprawl and other security issues it arises. - Teams Ownership and Membership
If you set up the right membership and ownership policies, you can better monitor teams and private channels and control what information or data is being shared. Teams’ owners can remove members, change settings, add guests, and perform administrative tasks.
Configure data security features
Office 365 provides a few additional features to secure your data or information. They are:
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
It helps identify sensitive data such as credit card numbers and prevents accidental exposure to reduce the risk of data breaches. You can set up DLP controls according to the sensitivity label. It blocks unauthorized users from accessing or sharing critical data in a private chat or Team’s channel. To secure your data, you can apply these policies to guests or external users. - Use Sensitivity Labels
The Microsoft information Protection (MIP) sensitivity labels allow you to protect Teams’ data without affecting user productivity and collaboration. It also protects teams from third-party applications and enforces protection settings with watermarks or encryption. Such as, if you label a team group as “Private,” it gets encrypted means users outside your organization can’t access that Team.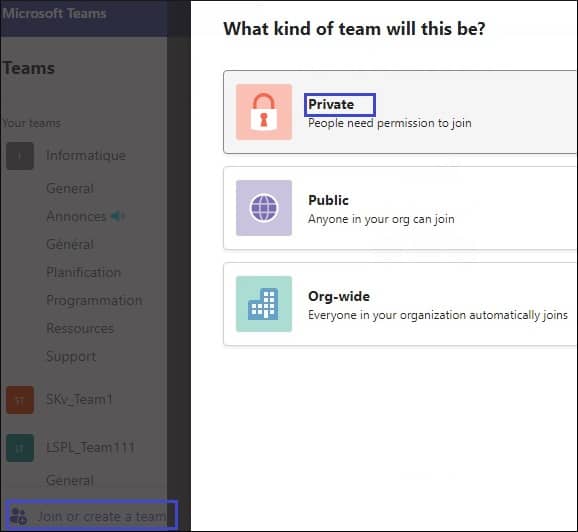
Configure data access control for Teams
Data access control is important in securing data and file sharing outside the organization. You can provide external as well as guest access to the Teams channel. Let’s discuss both these access controls in detail:
-
- External Access
By default, external access is enabled in teams means your users can collaborate with all external users. It grants permission to the Teams users from other domains to collaborate with users in your domain. It is useful when two different organizations want to work together. That’s why it has become necessary for organizations to configure and monitor teams’ external access over time. By the way, you can control external access only in specific businesses by changing a few settings.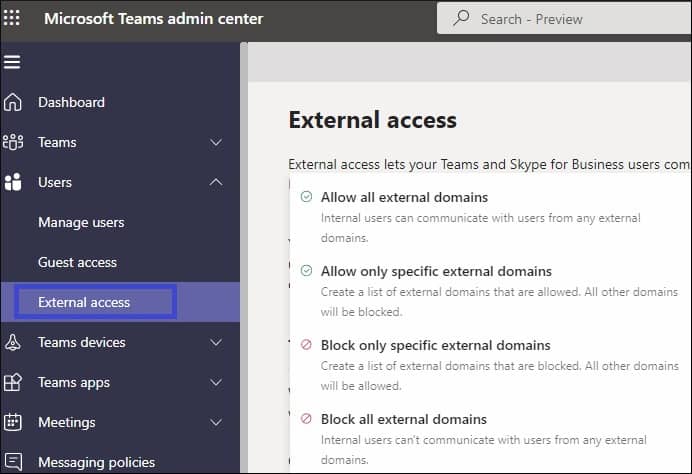
- Guest Access
Guest access means allowing an external user to be a part or member to participate in your chats, file sharing, and channels through a guest invitation process. Through this, you grant access to external users and govern access to your enterprise data.By the way, the administrator can disable guest access or govern the guests’ capabilities, such as whether they can edit or delete chats in channel posts, share files, etc. Configuring or monitoring guest access is crucial to avoid data breaches regularly.
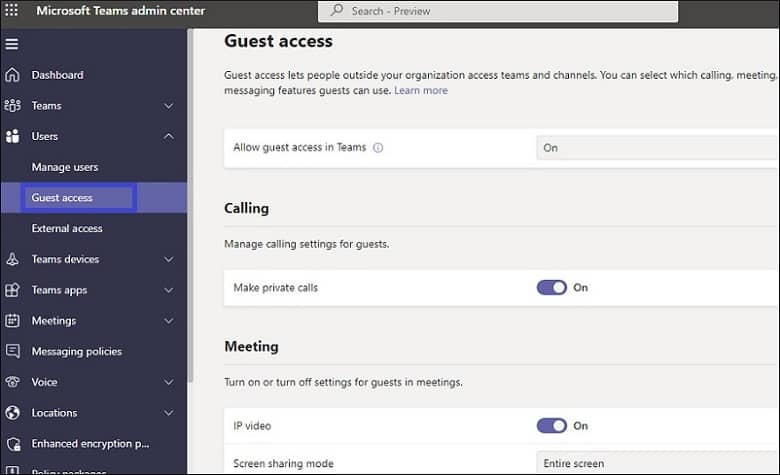
- External Access
Here are some other methods to control external or guest access in your Teams channels:
- Use the Lobby Feature
This feature can prevent external users from accessing your Teams meeting. Whenever external users try to access your meeting, they will be redirected to the virtual lobby, where they need to wait for admission. - Enable Private Channels within the Team
Create a private channel and add all team members and guests, but only team owners have the right to access it.
Monitor user activity regularly
Monitoring helps you in analyzing how users are interacting with Teams. You can use insights to check user behavior and what you need to change to achieve better Teams security.
Teams also provide limited monitoring capabilities to prevent blanket permission of third-party apps offered by Office 365 that require access to users and corporate data. Admins can pre-create a list of permitted third-party apps. If Team requires any non-listed app, they can manually check it before granting permission. It prevents teams from any external attack.
You can monitor teams’ activity on analytics and reports in the admin center.
Implement effective data management policies
If the sensitive information is still in the Team even after it has outlived its purpose, it presents a security risk, and there is a chance of data leakage or data loss. Use these three policies to manage data:
- Retention
Configure Teams retention policies for channel messages and chat and move them to SharePoint and OneDrive once the time is over to free up some space in Teams. - eDiscovery
It’s an Office 365 tool that allows you to identify and return electronic information or data to be used as evidence in legal matters. You can recreate the Teams conversations with this tool for the legal team. - Expiration
By setting an expiration date, you can manage the lifecycle of Office 365 groups. Even owners will be asked to renew their expired groups; if not done, they will be deleted permanently. Group owners or administrators can restore deleted groups within 30 days.
Advanced security measures for Teams login
When users log into Teams accounts, an extra layer of security can be added to ensure only authorized users have account access. Implementing the two techniques discussed below will boot Microsoft Teams Security.
- Multifactor authentication (MFA)
It is one of the most basic security measures that you must apply on every account be it Microsoft or any other cloud service. Setting up an MFA asks for another verification along with the traditional username & password. This helps in ensuring no unauthorized access takes place even if the password is compromised. - Conditional Access policies
They allow for more specific and controlled access, even more flexible than multifactor authentication. MFA works the same for everyone, while Conditional Access policies can be tailored to be more specific. These policies activate on events such as when a user tries to log in. Implementation of access policies can even deny user access based on perimeters like geographical location.
Conclusion
Microsoft Teams has become important to business continuity, and with its growing usage, it becomes essential to understand all significant areas of Microsoft Teams’ security. I hope this blog gives you an overview of all major areas required for Microsoft Teams security. However, even after executing all the techniques discussed in this blog, we recommend you maintain a consistent backup of Teams data to secure data in any calamity. For a complete Teams backup including Team, channels, chats, posts, notes, files, etc. use Kernel Microsoft Teams Backup tool. The tool maintains complete data integrity and preserves original account permissions & configurations. All data is backed up over a secure connection.