Read time 8 minutes
VMDK is a type of virtual disk format that has been created by VMware company for the diverse types of servers which include VMware ESX Server, VMware GSX Server 3.x and 2.5, VMware ACE, VMware Player, etc. VMDK is but an imitation of the physical hard disk, and the more efficient the Virtual Disk, the better the Guest OS will run. Additionally, since the IT sector seems to be moving towards what is called ‘Server Consolidations,’ the necessity of knowledge of managing and running of the Virtual Machine becomes more critical. To control the most vital configurable aspect of a virtual machine are CPU, Memory, and Disk frequently, there is a necessity of Virtual Disks (which depend on the requirement or operation of space by the workload present in the Data Center).
Need to move
Having spoken the above, as an introduction to what VMDK file is and the importance of the VMDK file; the present topic deals with how the user might be able to change the vmdk file location. But why would anyone want to do that? Well, to start with, it is essential to know that you can change the position on the same host system. To add on, the VM can also be moved to a different operating system. What the movement entails is that it is also the movement of the files which make up the virtual machine. vmdk file location is changed due to the following reasons:
- Moving a VM disk using a single VMware product to an unlike platform using a different VMware Product.
- Troubleshooting problems that entail or emerge high disk-space use.
- In the case of cloning a VM.
- If you are backing up your Virtual Machine.
Now, that we see why we need to move vmdk file location let us now focus on the very topic of our discussion, namely how to run the file location.
How to move the VMDK files?
Moving VMDK files to a different location or host have satisfied prerequisite which needs to be followed diligently before running the VMDK file to a new or different host. The following are the prerequisites that you must pay heed to, before moving:
- Firstly, try to become familiar with how Workstation produces UUIDs for move VMs. (P.S. UUID is a 128-bit number which is used to identify an object or entity on the Internet uniquely)
- Secondly, please acquaint yourself not merely on the advantages of moving VMDK File but also the disadvantages associated with it, namely:
- The guest operating system might cease to work correctly when the movement of the virtual machine to a host system which has significantly different hardware.
- Workstation 7.x and later versions of the virtual machines sustain up to eight-way virtual symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) on the multiprocessor host-systems. The user is permitted to Assign up to eight virtual processors to the virtual machines that run on the host systems and have at least a pair of logical processors. In case the user attempts to assign two processors to a virtual machine which runs on a uniprocessor host system, a warning message pops up. The user may show disregard for this message and assign two processors. However, the user needs to move it to a host with two logical processors at the least, before powering it on.
- Moreover, the user can move a virtual machine from a host of the size of 32-bit to a host of 64-bit. But the same person cannot run VM from a 64-bit host to a 32-bit one except for the 32-bit host having a supported 64-bit processor.
- Thirdly, in case of moving a linked clone, you will need to verify if the clone can access the parent virtual machine. Please follow these instructions, concerning the movement of the vmdk file location:
- In case the user is moving a linked clone or moving its parent virtual machine, he/she would need to assure that the clone can access the parent virtual machine.
- The user needs to make sure that the Workstation can locate the original virtual machine. If the Workstation is incapable of finding the original virtual machine, it cannot power on a linked clone.
- In case of a disconnected laptop, in which the user wishes to make use of a cloned virtual machine, it is necessary that the user must ensure the clone used is a full clone or must move the parent VM to the laptop.
- Backup copies of the files that are in the directory for the virtual machine that is being moved.
That being clear, we now proceed to the procedures that are followed to move vmdk file location to a new place. Given below are the Do It Yourself Steps:
- To begin with, make sure that VM files have been stored within the VMs directory because some of this file dwell outside the list.
- Now close or shut down the guest operating.
- Again, power-off the VM.
- Copy VM files to a new location (Note: in case the data have been moved to the same host system, remove the virtual machine from the library and then select File, go to Open and Browse to the VM configuration file in the new location.
- After moving the Virtual Machine to a different host system start Workstation, select File then press Open and browse to the virtual machine configuration file.
- When convinced that the VM works perfectly in the new location, delete virtual machine files from the original site of the data.
(To be Noted: In case the VM does not work correctly on them, the user needs to verify if the VM file has been copied whole)
Read also: Difference between VHD and VMDK files
If the DIY steps do not help you, yoou will require third-party software to move the vmdk file location to a new place. One such software is Kernel VMDK Recovery. The Software has been created to efficiently extract all types of data irrespective of them being either docs or audio files, or media files, and more. Moreover, the software can search for examples of the document with its Find option. However, there are some other free VMDK recovery methods also available to try.
The Software can be used straightforwardly namely,
- Browse and then select corrupt VMDK file.
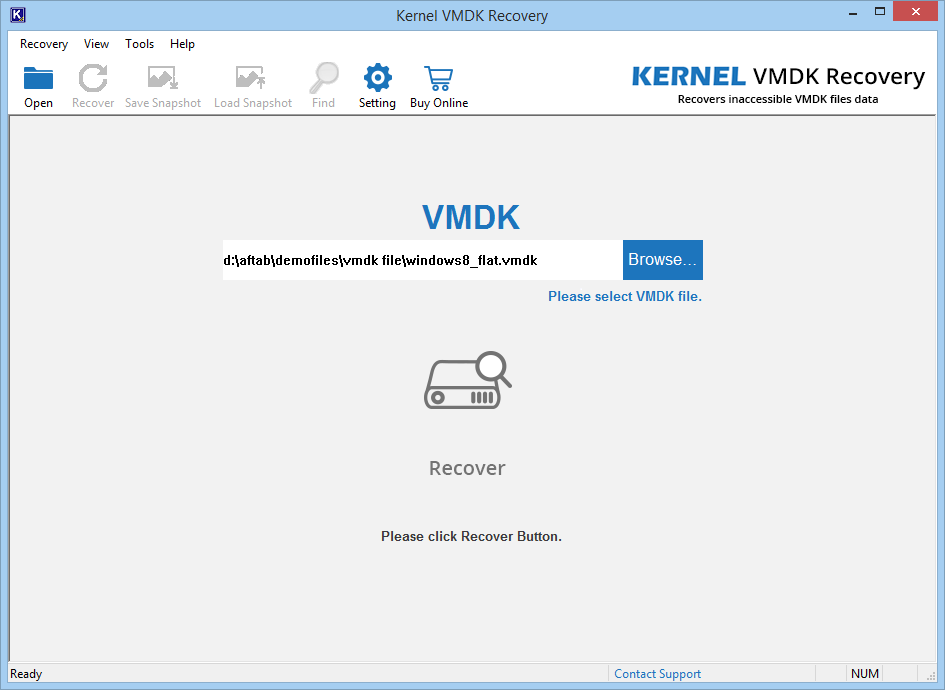
- Click Recover

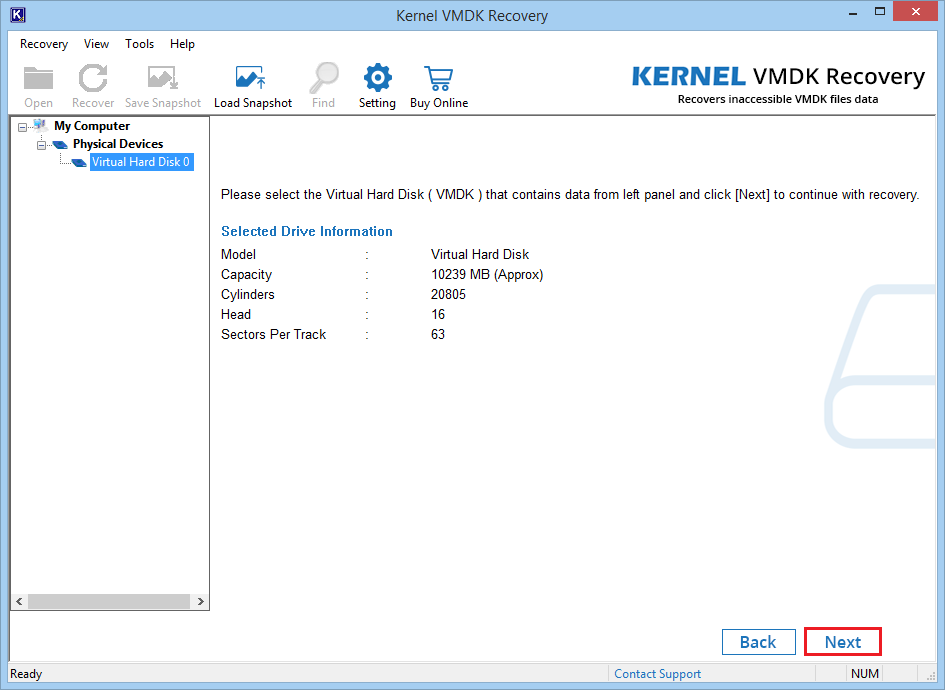
- Whole drive information is seen. Click Next.
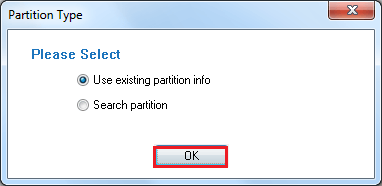
- Select Partition Type between w of the options. Then click Ok.
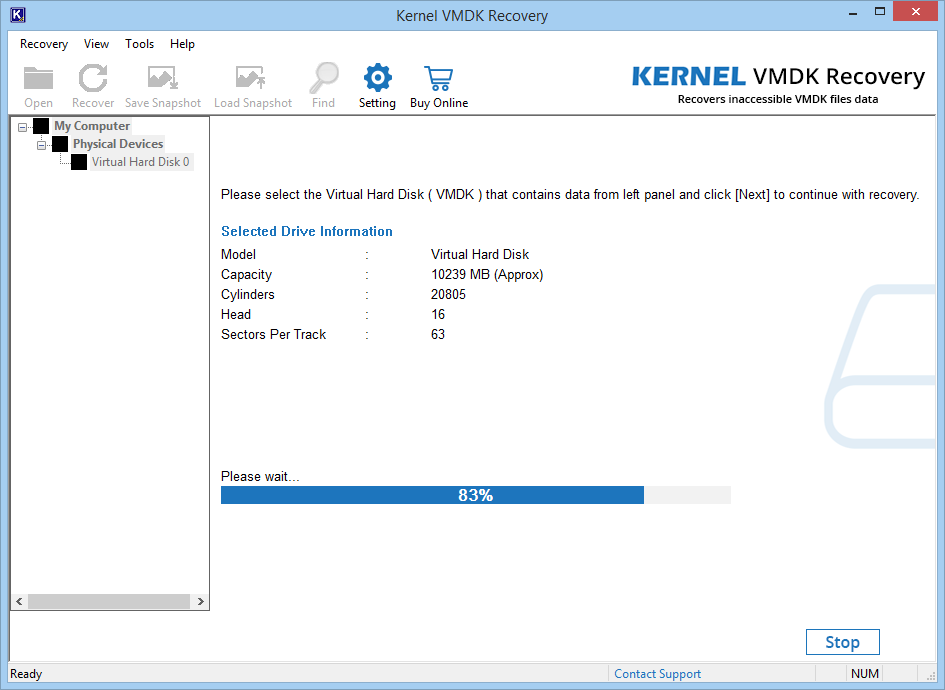
- Select ‘Partition Recovery.’ Press Scan.
- After the scanning process is complete click Next. Select the items that need to be recovered. Click ‘Repair.’
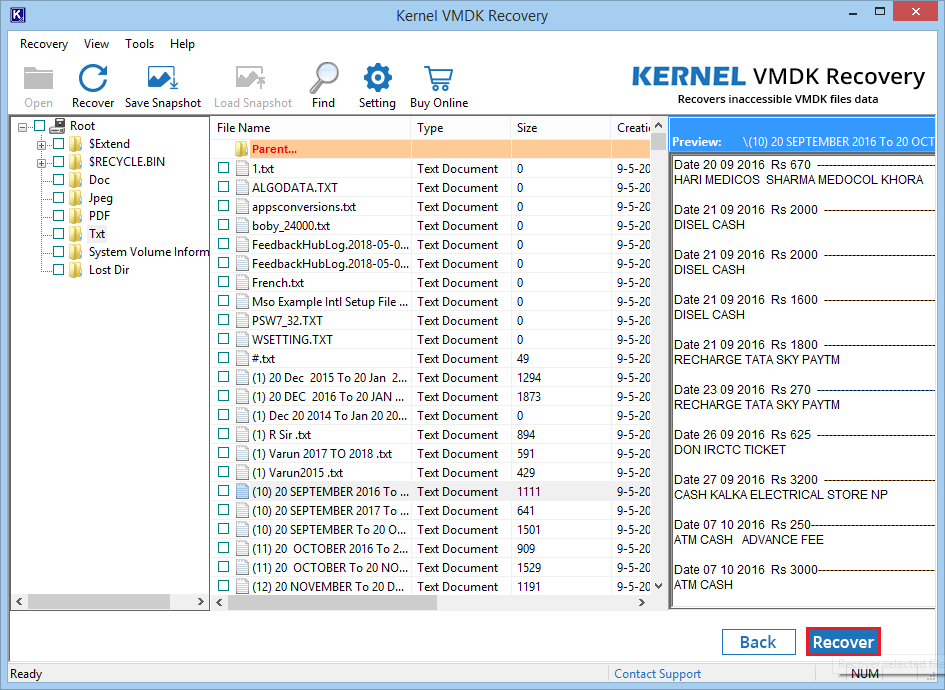
- Browse and Select Saving Path then click OK.
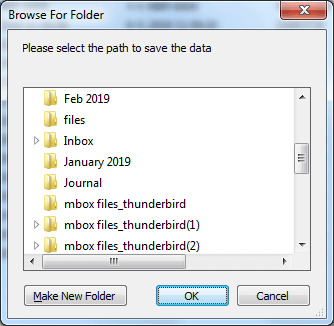
- Saving process starts.
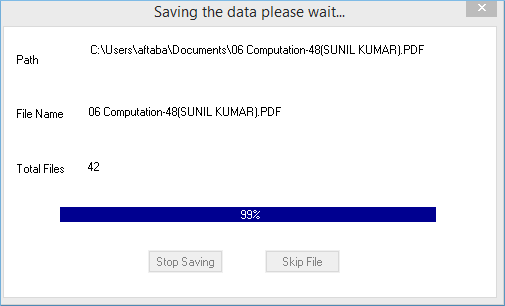
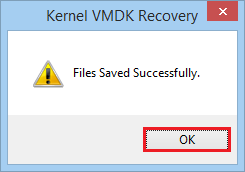
- When Complete, message ‘File saved successfully’ appears.
Conclusion
Summarizing all of it, the vital aim here has been to provide a comprehensive steps to our readers concerning the change of the VMDK file to a new or different location. We hope that these tips will help our readers to Change VMDK File Location to Different Data Stores in a natural, practical and cost-effective manner.








