Read time 7 minutes
Despite the organization you’re from, business type and size, security is a top concern of every business in today’s competitive world. It is a fact that even cloud data is not completely secure; rather, it is highly vulnerable to malware attacks, phishing attacks, ransomware attacks, data breaches, hacking, and more such external threats. Most of the Microsoft 365 users are suffering from this currently as they have not followed even the basic security practices suggested by Microsoft.
To ensure your data, files, and devices are secured from the breaches, you must know the best security practices available for Microsoft 365. Let’s start understanding Microsoft security from the root.
Best practices for Microsoft 365 security
We decided to provide some essential information regarding these practices to help them work on a secure, breach-proof, and risk-free cloud environment.
Use Microsoft 365 Security Score
Microsoft 365 Security Score is an in-built service from Microsoft, by which users can analyze the current settings and history to get insights compared to recommended actions for Microsoft 365 identities, applications, data, devices, and infrastructure. It generates reports with details based on the performance and provides a security score. It provides you a security analytics dashboard that allows you to safeguard your Office 365 data using the security score according to the top-industry standards.
This security score compares the Microsoft 365 user security settings to the standard practices by Microsoft. Using Microsoft 365 score helps users to update the security of their Microsoft 365 accounts.
Provide training to users
Office 365 users should be provided with advanced training on the features, interface, and security.
They should be trained on essential Microsoft 365 security practices like creating strong, unguessable passwords for the user mailboxes, enabling Windows system protections like Firewalls, Antivirus or Antimalware, using accounts protections tactics, and more.
Set multi-factor authentication to accounts
The Office 365 account is password protected, but that is not enough due to increasing hacking activities and breaches in the digital world. The recommendation here would be to enable the multi-factor authentication for the Office 365 user accounts.
Multi-Factor Authentication means users can sign into the Microsoft 365 account only after completing multiple authentications for the same account. The authentications can be OTP verification from the phone number or an email address other than the current one. It is also known as 2-step verification. It is good to protect your account from unwanted intruders and hackers.
It is needed to enable Security Defaults in Microsoft 365 to enable multi-factor authentication. In the latest subscriptions, it is enabled by default. Though, here are the necessary steps to enable it manually.
- Sign in to your Microsoft 365 account with administrator credentials (username and password).
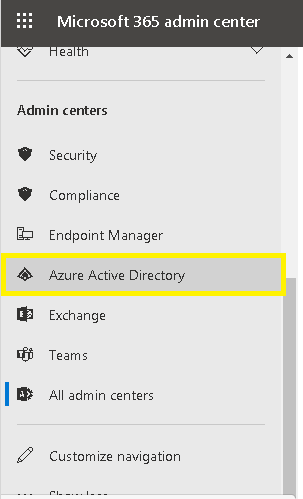
- Click on Admin Center and navigate to Show All>Admin centers>Azure Active Directory
.
- In the opened Azure Active Directory admin center, select Azure Active Directory and then select Properties option.
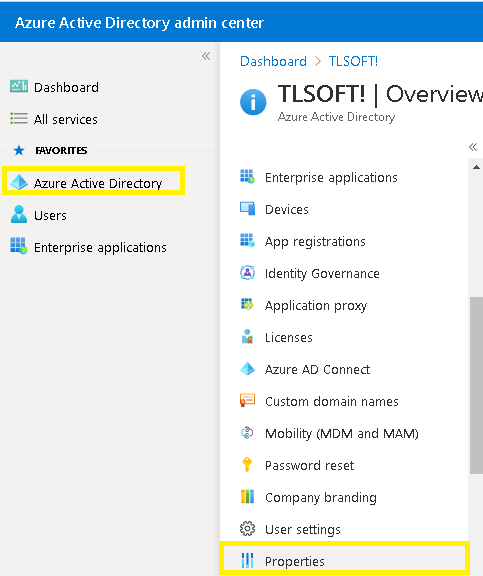
- Next, click on Manage Security defaults option.
- To enable the Security defaults, click on Yes and then click on Save to save this setting.
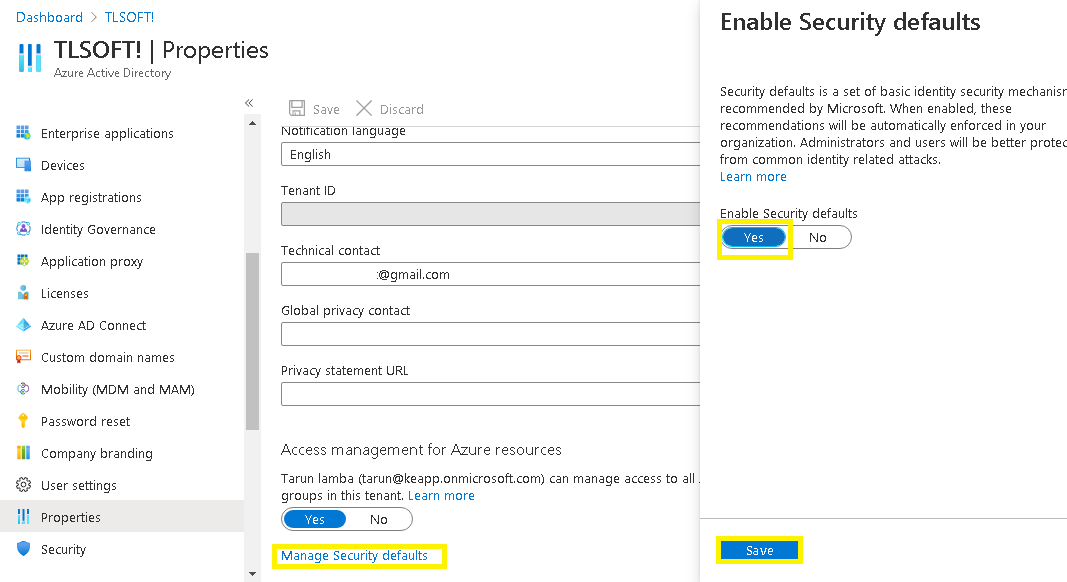
After enabling security defaults, you can now enable Multi-factor Authentication or 2-step verification for your Microsoft 365 account with the Account Settings feature.
Manage access permissions
Managing permissions and access to Microsoft 365 data can help you avoid threats and vulnerabilities. Allows least privileges to the user accounts and grant rights only to the data that is necessary rather than allowing users to access all the data whenever they want to.
Security practices for Microsoft 365 Account data
There is a great threat to email messages and their confidential data from intruders in some way or the other. Here, we are suggesting some effective security practices to protect the data of the organization.
Use Office message encryption
Encrypted messages are those messages which can be read or used by the intended recipients only. Microsoft 365 users can encrypt the emails before sending it to the desired recipient within email services like Yahoo, Gmail, Outlook.com, and more.
To encrypt the email, users just need to click on Options while drafting the email and then follow Permission>Encrypt. There are other permissions options as well, like Do Not Forward, Confidential/All Employees, and Highly Confidential/All Employees, which users can apply. The recipient has to enter a passcode or sign in to access the encrypted email. So, encrypting the email message is another great security practice to protect Office 365 account data from misuse or breach.
Disable the Autoforward feature
The Auto Forward setting can be easily misused. But the user may not have any knowledge about this.
It is a wise practice to avoid this auto-forwarding of emails, and the best way to do it is creating a new rule and then restricting the Auto-forwarding in the settings.
- Sign in to your Microsost 365 account and open Admin Center.
- Follow Admin Centers>Exchange to open the Exchange Admin Center.
- Select mail flow category from the left panel and then click on rules.
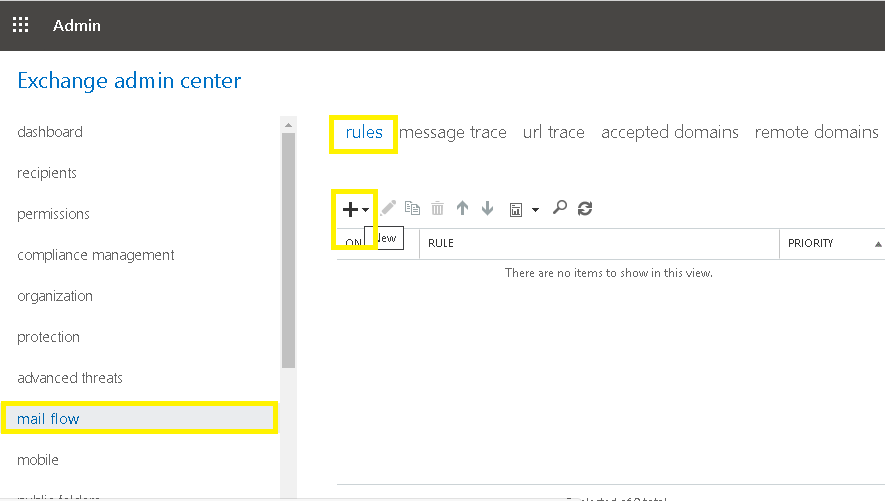
- Click the + icon to create a new rule. Click on More options.
- Apply settings with Reject Auto-forward emails to external domains and add conditions as per the requirement.
Add a Name and use Block the Message action for Rejecting email for certain recipients and add desired conditions.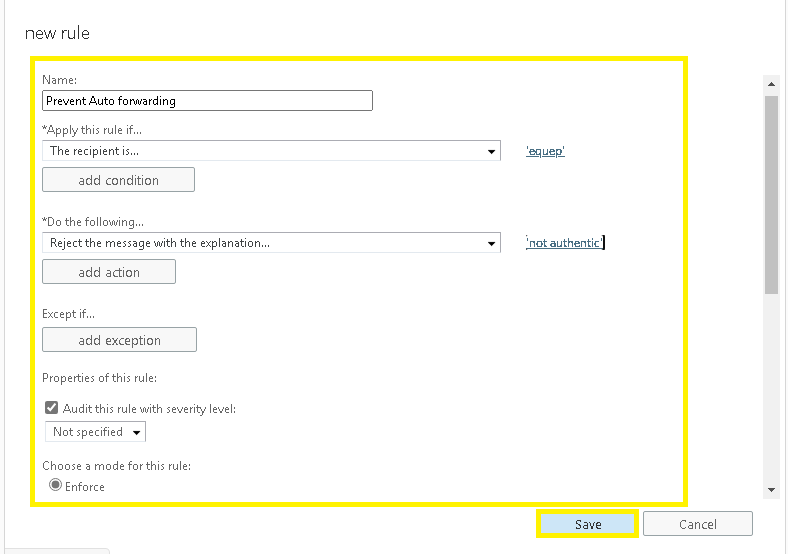
- Click Save to save settings of this new rule for your Microsoft 365 account email flow.
Enable data loss prevention
DLP, or data loss prevention, helps restrict users from sharing sensitive information about your organization externally. This is crucial in protecting information like financial data. You can use the Compliance Center within Office 365 to enable the Data loss prevention policies and there define the type of information you want to protect. It will ensure that a specific action or alert is sent to the Office 365 administrators as soon as the restricted information sharing is identified.
Configuring advanced protection against malware/ransomware
Microsoft 365 Security & Compliance Center includes advanced options to protect from malware and ransomware.
For protection against malware, users can use the Threat Management Policy and block those common file extensions to Protect Office 365 Mailbox from Ransomware Attacks, which generally include malware.
The Microsoft 365 Advanced Threat Management feature also allows users to set up ATP anti-phishing policy, ATP Safe Attachments policy, and ATP Safe Links policy to prevent Microsoft 365 content from harmful phishing attacks, malicious attachments, and infected links respectively.
How to save emails from ransomware attacks?
To save the precious emails from undesirable ransomware attacks, users can create a mail transport rule and apply settings and conditions over suspicious emails like this.
- Open the Exchange Admin Center from the Admin Centers category in the Microsoft 365 Admin Center.
- Go to mail flow>rules and click on the plus icon to create a new rule.
- Click on 4 stars to open More options.
- Apply the following settings for mail flow:
- Block file types that could contain ransomware or other malicious code
- Warn users before opening attachments of Office files
- Add conditions for the emails and attachments as per your wisdom and requirement.
- Now, your emails and attachment files are ransomware protected.
We hope you have learned some advanced security services provided by Microsoft 365. To have permanent security for the Microsoft 365 data, users can perform regular backups of its data. While Microsoft does not provide much reliable backup solutions that could help you easily save data, Kernel Office 365 Backup & Restore solution allows taking Office 365 data backup efficiently. Simply select the mailboxes that you want to backup and save them to PST, MSG, EML, or other file formats to your system without altering the integrity.
Conclusion
Keeping your data in a secure environment helps you dodge risks to your revenue as well as the business reputation. Following the security practices like enabling multi-factor authentication and data encryption might help you prevent data breaches to an extent. However, it is also equally important to store most recent backup of your data to avoid potential data loss if any cyberattacks happen. Kernel Office 365 backup & restore tool is a great aid in backing up Office 365 data efficiently.