Read time: 8 minutes
Ransomware is a unique type of malware that encrypts the user’s computer and demands money from you. The payment is generally made through Bitcoin after which the computer is unlocked. The cybercriminals who attack your computer set a deadline for making the ransom payment or else they threaten to lock the system forever, if the payment is not done within the deadline.
The following is an example of WannaCry attack that had encrypted thousands of computers in 2017 in more than 150 countries. The situation left the organizations in stress to come up with a quick and reliable solution to regain access to their sensitive business data. This article will share some backup solutions to safeguard data even in cases of cyber breaches.
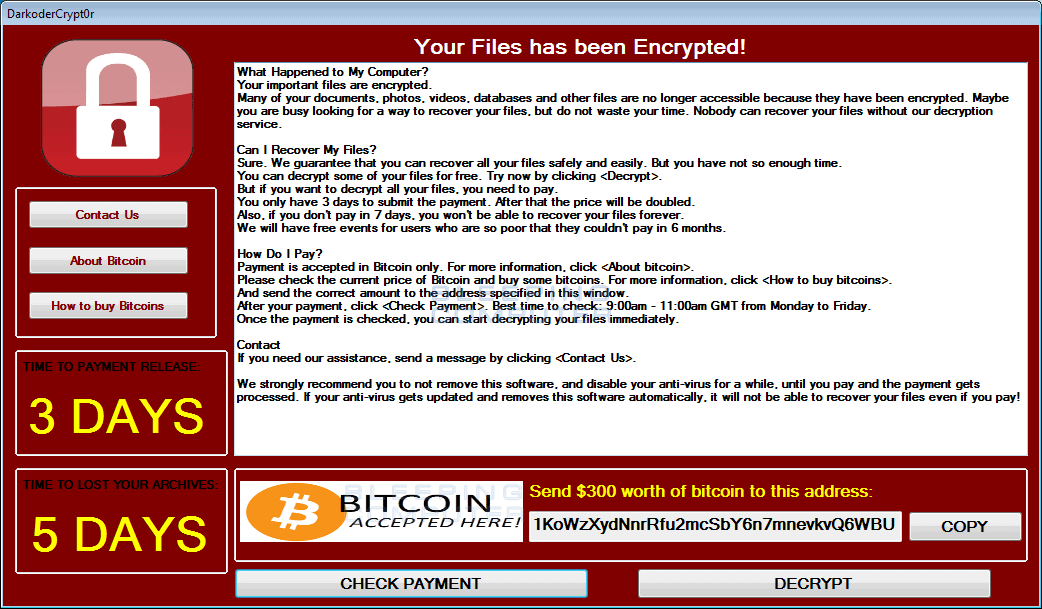
How does ransomware work? Are there different kinds of ransomware?
Ransomware attacks happen via many different modes, like spam emails, phishing emails, websites, drive-by downloads, etc. Once it infects a network computer, it can infiltrate into other computers of the network and to block access to documents, photos, media, technical information, financial information, and other types of data.
There are different types of ransomware, and they infect users and their data as per their type. By knowing the types of ransomwares, you can learn how not to become a victim of it. Different types of ransomwares are:
- Cryptoware: This is the most common and dangerous form of ransomware that encrypts your files, folders, and hard drives.
- Lock Screens: Lock screen Ransomware is also known as lockers or non-encrypting ransomware. It locks you out of your system so that you cannot access it. It doesn’t encrypt them, but it restricts the user entry.
- Raas: Raas, also known as Ransomware as a Service, is an insidious ransomware created by the hacker anonymously. In this type of Ransomware attack, the hackers provide a service in the form of software to decrypt the data only in return of a ransom.
- Leakware: It is also known as Doxware or Extortionware. This type of Ransomware threatens to publish the stolen data and information of the user.
- Scareware: It is a deceptive type of ransomware that is presented to the user as a computer program that fixes some issues and asks the user to buy it to get protection. It mostly guises as an antivirus, and once the user downloads it, it creates more problems.
- Mac Ransomware: As the name suggests, this type of Ransomware attacks the Mac Operating Systems. KeRanger is a notorious Mac Ransomware that penetrates the systems via an app called Transmission.
- Mobile Ransomware: This type of Ransomware infiltrates mobile devices through drive-by downloads or a malicious fake app, which, after installation, takes over the user data.
Who can be a victim of it?
The major targets or victims of this fraud are mostly organizations regardless of their size. But the specific things about these organizations are that they have a smaller IT and security team, have very sensitive data, and so are ready to pay quickly.
Here are the industries that are the prime targets of these cyber criminals.
- Healthcare organizations
- Human Resource departments
- Financial institutions
- Government and other public sector agencies.
- Academic institutions
The attackers can even misuse the data collected from such an organization and even sell it for different purposes.
How do hackers do it?
A Ransomware attack is not an easy job and is performed after full-fledged planning. It comprises many steps that the hackers perform minutely without being noticed:
- Entering the network: First, the hackers enter the user’s environment via spam emails or phishing emails. Once entered, they get installed on the user system.
- Creating a cryptographic key: Once installed on the system, the Ransomware generates a cryptographic key for the system.
- Encryption of files: Now, Ransomware starts encrypting everything it comes across. This includes encrypting everything on the network or the local server, leaving no file unharmed.
- Coercion: Once the encryption is done, Ransomware starts using different tactics for putting pressure on the user for paying. This includes showing notification or text, demanding the user to pay to get access to their data back.
- Decryption: The last stage is when the user is desperate to get control of his data and pays the demanded ransom. Finally, the hackers may or may not decrypt the data and provide them the access. However, there is no guarantee that the user will ever get back access to their data.
How can backup solutions help?
As per surveys, the number of Ransomware attacks are growing day by day, and the best way to protect yourself from it is by being proactive and taking appropriate precautions. Let’s see how backup solutions can help against ransomware attacks.
- Copy and store the backup
A good way to secure your data from ransomware is to copy the data on an external drive and store it offline. This way, you can have all your data at some other place, which is safe because it is offline, and no ransomware can access it. - How can Cloud backup help?
Keeping a backup on the Cloud is a good precautionary measure against ransomware. Windows data can be backed up on platforms like OneDrive and SharePoint Online (Office 365). And you can easily access your data on the cloud through the internet.
Best practices against cyberthreats and ransomware attacks
Learning about the best practices to take SharePoint backup helps in keeping your organization’s critical data safe against cyber threats, malware, and ransomware attacks. It also firms your standing amongst your customers and shareholders. Here’s what practices you can follow:
- Update operating system
Ensure that the operating system and applications installed on the computers and laptops within your organization are up to date. Outdated software has the potential of allowing attackers to make you vulnerable to attacks, therefore, always stay updated. - Strong authentication
Consider implementing multifactor authentication and use strong password policies for all endpoint users working within your organization. Employing multi-factor provides additional security using verification methods like biometric or one-time-password. - Strategies to detect and prevent attacks
Always have cyberattacks detection and prevention strategy in place. The combat strategy against these attacks should include real time monitoring of network traffic and system logs and behavioral analysis for any risk patterns, and other significant actions. - Multilayer security control
Multi-layer security control such as antivirus software, intrusion detection and prevention system, and firewalls, help in guarding the endpoints against cyber or ransomware attacks. - Use immutable storage
Immutable storage or WORM (Write Once Read Many) is a storage that keeps data within a bucket and secures it from further alterations. This storage ensures that the backup you’ve taken remains unchanged while preventing ransomware attacks. - Test backups regularly
Taking backups is not enough, you need to regularly test and check it for consistency. This will help you establish if the saved backup is operational and can be used to restore the data later on.
Reliable solution for to backup cloud data
Kernel Migration for SharePoint is one of the most effective solutions to backup data from SharePoint to local or NAS drive. You can also migrate data from legacy systems to cloud with this automated SharePoint migration tool. Prime features of the tool include:
- Download granular SharePoint backup of all the files, lists, libraries, and other content.
- Backup data from your Microsoft Teams chat and save to your preferred location.
- Migrate data to Google Drive or OneDrive to secure against cyber attackers.
- Manage permissions and apply role based access control to keep the data safe and secure.
- Backup data from cloud storage platforms and store it to the SharePoint platform.
Transferring your organization’s data to a cloud-based platform like SharePoint makes it more manageable and accessible to your team. The latest release offers various advanced features in SharePoint. During the migration process, none of the data files go missing and it also provides pre-migration analysis to avoid any possible errors. The tool easily proves how the backup solutions can help against ransomware attacks.
Conclusion
In this blog, we discussed in detail what ransomware is and how one can use backup solutions to secure their data from ransomware attacks. We have also mentioned a third-party tool, Kernel Migration for SharePoint which backup and migrate all your precious data securely. The tool can even help you with Teams backup and Microsoft Teams chat backup.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ans: If the backup available on your device before the attack was healthy and consistent, follow the given steps:
1. Evaluate the breach timeline to determine the effect of the attack on workloads.
2. Recognize the last clean recovery point created prior to the incident.
3. Find out the data retention period and if you need more time to restore from the attack, extend the retention duration.
4. Recover data to an isolated and secure location and restore a batch of data first for healthy recovery points.
5. Scan the restored data to discover infection and verify that it’s not compromised.
6. After establishing that the data is clean, you can implement it within the production system.
Ans: To prevent deliberate deletion or accidental removal of data, you can implement soft deletion. It permits retention of backup data for 14 days to help you recover it before it’s permanently removed from the system.
Ans: Following are a few strategies that can help you prevent data loss against ransomware attacks:
1. Follow 3-2-1 backup rule to protect data, which means create three copies of your data and store two copies on different storage with one copy kept offline.
2. Implement multi-factor authentication on the backups to secure them.
3. Use automated backup solutions to regularly take backups without manual intervention.








