For any organization that values its security and confidentiality, setting up an admin account in Exchange Server is an essential activity. Access to important Exchange Server functionalities can be granted with the use of a strong admin account. But to create an admin account, you must fully comprehend all aspects of the Exchange Server environment. We are here to offer a thorough tutorial on how to set up a reliable admin account in Exchange Server, with all the processes and commands necessary. Regardless of your level of skill, we will assist you in creating an admin account that is appropriate to your business's needs.
- Constant support to the user accounts and clients.
- Maintaining the performance of the Exchange Server at the highest level.
- Upgrading the infrastructure of Exchange Server whenever required.
- Removing the mail-flow issues and improving it.
- Update the Exchange Server version.
- Perform the backup and restoration operations.
For better collaboration and communication, the administrator creates multiple groups and assign user-accounts to these groups. Another major responsibility of an Exchange Administrator is to perform troubleshooting whenever a disaster occurs. That's why the role of the Administrator is too important for the organization. Exchange administrator accounts have more rights and permissions than a regular user account. Here, we will explain how you can create an Exchange administrator account.
Exchange administrator accounts have more rights and permissions than a regular user account. Here, we will go through a detailed narration to know about an Exchange administrator account and how do you can create one.
First, let us go through the Step-by-Step procedure of creating an admin account and assigning administrative roles:
- Login to Exchange Admin Center.
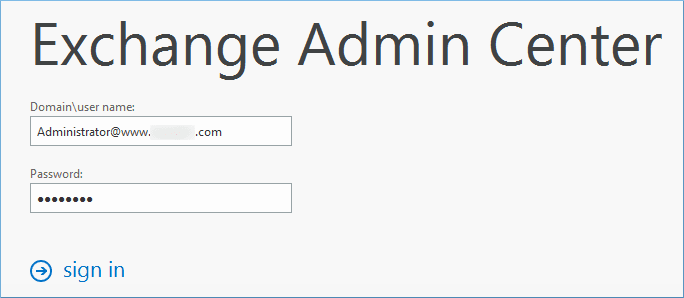
- In the permissions category, go to admin roles, and then select the category of Organization Management. Finally, click the Edit button.
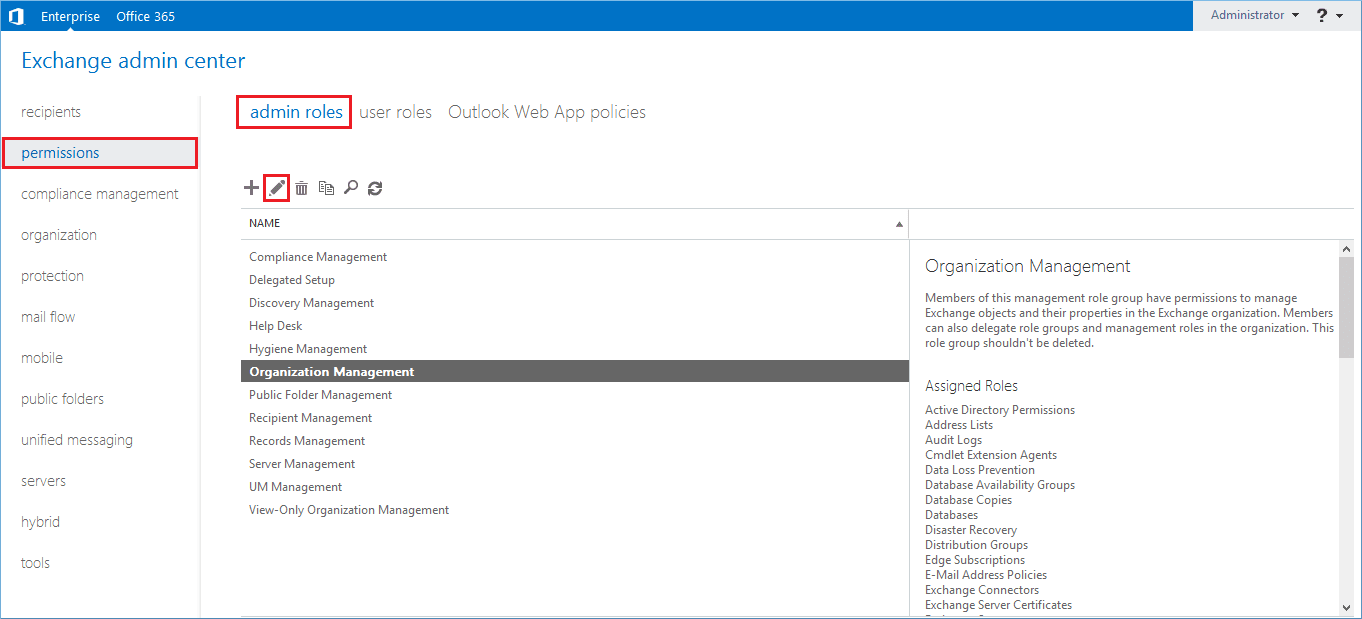
- Click the Add () button to add the member to the respective role group.
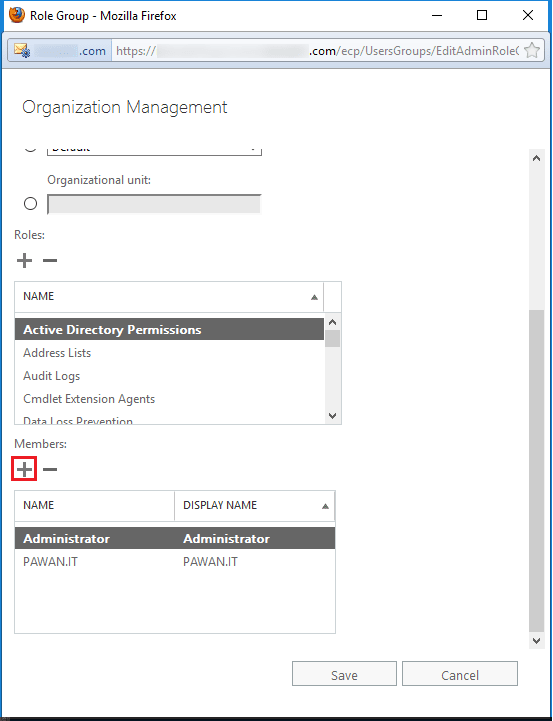
- Select the user which you need to add as an administrator. Click the Add button and then click OK.
- The new user is now a member of the Organization Management. Click the Save button.
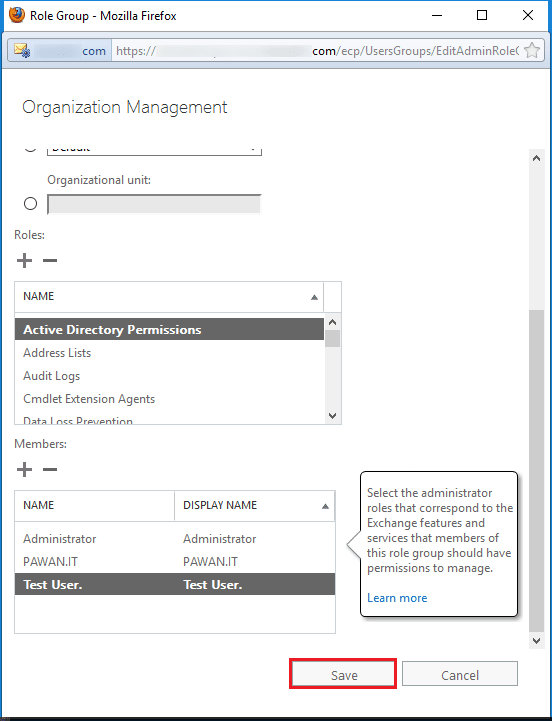
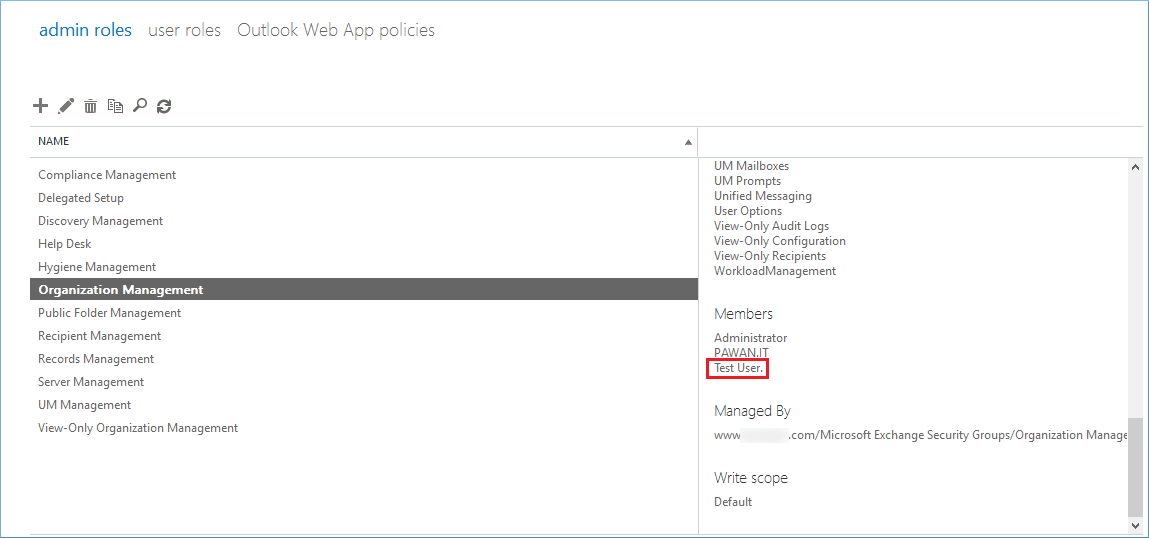
- You can see the new user in the list which has all the rights of the group.
After creating an administrator account, you should go ahead with understanding the role-based groups. An administrator should have at least one role assigned to it. It can also have more than one role to perform multiple jobs in the Exchange Server environment.
For easy management of roles, Microsoft has created role groups which are special universal security groups. When the role is assigned to a group, then all the permissions associated with the role are automatically attached to the group members. Here is a brief list of various built-in role groups which the administrator can become a member.
Organization Management: The administrator members of the Organization Management will have administrative access to the Exchange Server and can perform almost all managerial tasks.
View-Only Organization Management: Administrator members of this group can view the properties of any object in Exchange Server.
Recipient Management: Administrator members of this group can create or modify Exchange Server recipients within the Exchange environment.
UM Management: Administrator members of this group can manage the Unified Messaging service configurations and settings.
Records Management: Administrator members of this group can modify the compliance features like retention policy tags, message classification, and mail flow rules.
Discovery Management: Administrator members of this group can search the data in the entire Exchange Server environment based on a specific criterion.
Public Folder Management: Administrator members of this group can manage and configure public folders in the whole Exchange Server.
Server Management: Administrator members of this group can modify server configurations for transport, unified messaging, client access, mailbox, and features like certificates, database copies, send connectors, virtual directories, etc.
Delegated Setup : Administrator members of this group can deploy the servers which were earlier provisioned by a member of the Organization Management Role group.
Compliance Management: Administrator members of this group can manage the compliance settings based on their Organization policy.
Conclusion
So, this is the whole process of creating an Exchange administrator account and assigning roles for them according to the tasks it must accomplish. You should check the permissions of each role group and then add the administrator to it.
