How to increase the bad item limit in Exchange 2010?
Aftab Alam
 |
Updated On - September 27, 2023
|
Updated On - September 27, 2023
Read time 4 minutes
When performing a migration of an Exchange Server, whether it’s to another version of Exchange Server or Exchange Online, the crucial step is executing the move request to successfully conclude the migration process. The Move Request operation involves the utilization of numerous parameters and switches, each assigned a specific task. Among these parameters, there is the “Bad Item List,” which plays a pivotal role in governing the migration’s handling of problematic items.
The Bad Item List parameter is instrumental in setting a threshold for items that are deemed “bad” during the migration. In essence, an item qualifies as “bad” when the Move Request encounters difficulties in migrating it. It’s important to choose an appropriate bad item limit as part of your migration strategy. However, if this limit is exceeded despite your initial selection, you may encounter the following error message:
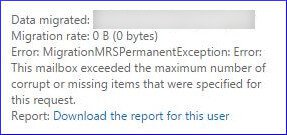
The error denotes that the number of corrupt items has more than permitted and so you need to update the limit for a smooth migration. Run the cmdlet given below to change the bad item limit for the move request if following –
When the request is executed, it permits the omission of up to 10 corrupted items during the migration process. However, if the number of corrupted items exceeds this threshold, an error will be triggered as described above. It’s important to note that there is no predefined default value for this parameter, allowing you to input any desired limit for handling corrupted items. Microsoft recommends exercising prudence by setting a reasonable value below 10.
The error is attributed to corrupt items within the Exchange Database. When initiating a move request, it will automatically detect and omit these problematic items during migration. However, once the threshold for corrupt items is reached, an error will be promptly displayed. This occurrence will temporarily halt the migration process, necessitating the implementation of the necessary corrective measures to resolve the issue.
Here are some manual methods which you can use to remove the error
After receiving the error, you should update the move request which you had created earlier. Increase the bad limit to a higher acceptable limit. If you increase the limit to more than 50, then you need to use the AcceptLargeDataLoss switch.
Now, you will not have to face the error up to 75 corrupt database items.
ESEUTIL is a free utility available within the Exchange Server which you can use ESEUTIL tool for identify the corruption and repair it using various switches. You can find the ESEUTIL tool at the following location –
C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V15\Bin
When you start the ESEUTIL tool, there are a list of switches which are useful for different jobs –
/D – It will defragment the database.
/K – It will verify the checksum of the database.
/P – It will repair the database.
/R – It will restore the database.
/C – It will hard recover the database.
/G – It will check the integrity of the database.
It will dismount the database from Exchange Server.
It will repair the database and remove all the errors.
It will mount the database back to the Exchange Server.
When you have repaired the database, you can once again start the move request and try to migrate the database to a higher version of Exchange or Exchange Online.
Both of the manual methods discussed above have their merits, but they lack a guarantee for resolving the issue of bad items. If the number of corrupt items exceeds the new limit, you may encounter the same error once more. In contrast, the ESEUTIL tool not only repairs the database but also has the capability to permanently delete corrupt items rather than attempting to restore them. Therefore, it is advisable to opt for a professional Kernel for EDB to PST tool that functions as an EDB file to PST converter for a more reliable solution.
Introducing Kernel for Exchange Server, a top-rated Exchange recovery tool that seamlessly accesses your database files from their original location and effectively addresses any corruption issues. Say goodbye to the hassle of running a move request post-recovery, as this tool autonomously migrates the retrieved items to your preferred destination. It stands as the ultimate solution to resolve the notorious bad item limit error whenever you encounter it.